Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi; Umeda, Miki; Motome, Yuiko; Murao, Hiroyuki
JAEA-Technology 2022-030, 80 Pages, 2023/02
Nuclear criticality benchmark analyses were carried out for TRIGA-type reactor systems in which uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rods are loaded by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-5. The analyses cover two sorts of benchmark data, the IEU-COMP-THERM-003 and IEU-COMP-THERM-013 in the International Criticality Safety Benchmark Evaluation Project (ICSBEP) Handbook, and effective neutron multiplication factors, reactivity worths for control rods etc. were calculated by JENDL-5 in comparison with those by the previous version of JENDL. As the results, it was confirmed that the effective neutron multiplication factors obtained by JENDL-5 were 0.4 to 0.6% greater than those by JENDL-4.0, and that there were no significant differences in the calculated reactivity worths by between JENDL-5 and JENDL-4.0. Those results are considered to be helpful for the confirmation of calculation accuracy in the analyses on NSRR control rod worths, which are planned in the future.
 phase to
phase to  phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformation
phase in zirconium alloy revealed by in-situ neutron diffraction during high temperature deformationGuo, B.*; Mao, W.; Chong, Y.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, H.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 242, p.118427_1 - 118427_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:64.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Amaya, Masaki; Udagawa, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 573, p.154110_1 - 154110_7, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Minato, Kazuo; Ogawa, Toru
Comprehensive Nuclear Materials, 2nd Edition, Vol.5, p.334 - 360, 2020/08
TRISO coated particle fuel has been developed for the high temperature gas-cooled reactors, which consists of microspherical fuel kernel and coating layers of pyrolytic carbon and silicon carbide. To improve the high temperature stability, the resistance to the chemical attack by fission products and the retention of fission products of the TRISO coated particle fuels, several types of advanced fuels were proposed and tested. Coated particle fuels for fast reactors were also proposed and tested. In this paper, fuel designs, fabrications, characterization techniques and fuel performance of these advanced coated particle fuels are systematically described. This is the updated version of the paper having the same title in Comprehensive Nuclear Materials published in 2012.
Sun, Y.*; Abe, Yuta; Muta, Hiroaki*; Oishi, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(8), p.917 - 925, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:53.85(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ueta, Shohei; Mizuta, Naoki; Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Honda, Masaki*; Saiki, Yohei*; Takahashi, Masashi*; Ohira, Koichi*; Nakano, Masaaki*; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 357, p.110419_1 - 110419_10, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)The concept of a plutonium (Pu) burner HTGR is proposed to incarnate highly-effective Pu utilization by its inherent safety features. The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. This paper presents feasibility study of Pu burner HTGR and R&D on the 3S-TRISO fuel.
Liu, J.; Dotsuta, Yuma; Kitagaki, Toru; Kozai, Naofumi; Yamaji, Keiko*; Onuki, Toshihiko
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR 2019) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2019/05
To decommission the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP), it is necessary to estimate the current status of fuel debris and predicate the possible change under various condition. Some microorganisms may enter the plant due to the seawater injection after accident and future defueling activity. In this study, microbial influence on fuel debris under aerobic condition was experimentally investigated. By culturing some bacteria in the presence of simulant fuel debris in liquid medium, the microbial degradation of fuel debris was observed.
 -UO
-UO
 -CO
-CO
 system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations
system and integration with JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculationsKitamura, Akira
JAEA-Data/Code 2018-018, 103 Pages, 2019/03
The latest available thermodynamic data were critically reviewed and the selected values were included into the JAEA-TDB for performance assessment of geological disposal of high-level radioactive and TRU wastes. This critical review specifically addressed thermodynamic data for (1) a zirconium-hydroxide system through comparison of thermodynamic data selected by the Nuclear Energy Agency within the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD/NEA), (2) complexation of metal ions with isosaccharinic acid based on the latest review papers. Furthermore, the author performed (3) tentative selection of thermodynamic data on ternary complexes among alkaline-earth metal, uranyl and carbonate ions, and (4) integration with the latest version of JAEA's thermodynamic database for geochemical calculations. The internal consistency of the selected data was checked by the author. Text files of the updated and integrated thermodynamic database have been prepared for geochemical calculation programs of PHREEQC and Geochemist's Workbench.
Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 5(5), p.18-00084_1 - 18-00084_9, 2018/10
To develop the security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) for Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR), R&D on zirconium carbide (ZrC) directly coated on yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) has been started in the Japanese fiscal year 2015. As results of the direct coating test of ZrC on the dummy YSZ particle, ZrC layers with 18 - 21 microns of thicknesses have been obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight. No deterioration of YSZ exposed by source gases of ZrC bromide process was observed by Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM).
Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Mizuta, Naoki; Goto, Minoru; Fukaya, Yuji; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 9th International Topical Meeting on High Temperature Reactor Technology (HTR 2018) (USB Flash Drive), 7 Pages, 2018/10
The security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) employs the coated fuel particle with a fuel kernel made of plutonium dioxide (PuO ) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO
) and yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) as an inert matrix. Especially, a zirconium carbide (ZrC) coating is one of key technologies of the 3S-TRISO, which performs as an oxygen getter to reduce the fuel failure due to internal pressure during the irradiation. R&Ds on ZrC coating directly on the dummy CeO -YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
-YSZ kernel have been carried in the Japanese fiscal year 2017. As results of ZrC coating tests by the bromide chemical vapor deposition process, stoichiometric ZrC coatings with 3 - 18 microns of thicknesses were obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight.
 (am) solubility at 25
(am) solubility at 25 C in the Ca
C in the Ca -Na
-Na -H
-H -Cl
-Cl -OH
-OH -H
-H O system; A Critical review
O system; A Critical reviewRai, D.*; Kitamura, Akira; Altmaier, M.*; Rosso, K. M.*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Solution Chemistry, 47(5), p.855 - 891, 2018/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:8.45(Chemistry, Physical)We have critically reviewed experimental data for Zr hydrolysis constant values for formation of several mononuclear and polynuclear species and a solubility product value for ZrO (am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
(am). We have determined new/revised values for the formation constants of Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH) (aq), Zr(OH)
(aq), Zr(OH)
 , Zr(OH)
, Zr(OH)
 and Ca
and Ca Zr(OH)
Zr(OH)
 , and the solubility product for ZrO
, and the solubility product for ZrO (am) after the critical review.
(am) after the critical review.
Muta, Hiroaki*; Nishikane, Ryoji*; Ando, Yusuke*; Matsunaga, Junji*; Sakamoto, Kan*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Oishi, Yuji*; Kurosaki, Ken*; Yamanaka, Shinsuke*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 500, p.145 - 152, 2018/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:77.27(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ueta, Shohei; Aihara, Jun; Goto, Minoru; Tachibana, Yukio; Okamoto, Koji*
Proceedings of 25th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-25) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2017/07
To develop the security and safety fuel (3S-TRISO fuel) for Pu-burner high temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR), R&D on zirconium carbide (ZrC) directly coated on yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ) has been started in the Japanese fiscal year 2015. As results of the direct coating test of ZrC on the dummy YSZ particle, ZrC layers with 18 - 21 microns of thicknesses have been obtained with 0.1 kg of particle loading weight. No deterioration of YSZ exposed by source gases of ZrC bromide process was observed by Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM).
 -radiolysis of nitric acid solution
-radiolysis of nitric acid solutionIshijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 16(2), p.100 - 106, 2017/05
Zirconium (Zr) has been used as a structural material at the spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant in Japan because of its excellent corrosion resistance against nitric acid solution. And the radiolytic hydrogen is known to be generated in the spent nuclear fuel solution. Zr is known to be highly susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. Therefore, evaluating the radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior of Zr in nitric acid solution (HNO ) is essential. In this study, immersion tests were conducted on Zr in nitric acid solutions under
) is essential. In this study, immersion tests were conducted on Zr in nitric acid solutions under  -ray irradiation to evaluate its radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior. Results showed that hydrogen concentration on Zr increased both in 1-3 mol/L HNO
-ray irradiation to evaluate its radiolytic hydrogen absorption behavior. Results showed that hydrogen concentration on Zr increased both in 1-3 mol/L HNO and pure water at 5 and 7 kGy/h after immersion. The amount of hydrogen absorption on Zr under
and pure water at 5 and 7 kGy/h after immersion. The amount of hydrogen absorption on Zr under  -ray irradiation had a direct correlation with the radiolytic hydrogen generation value in HNO
-ray irradiation had a direct correlation with the radiolytic hydrogen generation value in HNO . The results of glow discharge optical emission spectrometry, thermal desorption spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction result shows that the absorbed radiolytic hydrogen generated a hydride on the surface of Zr.
. The results of glow discharge optical emission spectrometry, thermal desorption spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction result shows that the absorbed radiolytic hydrogen generated a hydride on the surface of Zr.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Teshima, Takeshi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(2), p.233 - 241, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:51.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zr solubility in the presence of gluconic acid (GLU) and isosaccharinic acid (ISA) was investigated as a function of hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH
) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH)
and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH) (GLU)
(GLU)
 in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH)
in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH) (GLU)(GLU
(GLU)(GLU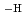 )
) in the alkaline pH region above pH
in the alkaline pH region above pH 10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10
10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10 - 10
- 10 mol/dm
mol/dm (M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH)
(M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 and Zr(OH)
and Zr(OH) (ISA)(ISA
(ISA)(ISA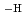 )
) were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH)
were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH) (am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
(am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
Kato, Chiaki; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1371 - 1379, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of crystal textures and the potentials in the anodic oxidation of zirconium in a boiling nitric acid solution were investigated to study the stress corrosion cracking of zirconium in nitric acid solutions. The growth of the zirconium oxide film dramatically changed depending on the applied potential at a closed depassivation potential (1.47 V vs. SSE). At 1.5 V, the zirconium oxide film rapidly grows, and its growth exhibits cyclic oxidation kinetics in accordance with a nearly cubic rate law. The zirconium oxide film grows according to the quantity of electric charge, and the growth rate does not depend on the crystal texture in the pretransition region before the cyclic oxidation kinetics. However, the growth and cracking under the thick oxide film depend on the crystal texture in the transition region. On the normal direction side, the oxide film thickness decreases on average since some areas of the thick oxide film are separated from the specimen surface owing to the cracks in the thick oxide. On the rolling direction side, cracks are found under the thick oxide film, which deeply propagate along the RD without an external stress. The cracks under the thick oxide film propagate to the center of the oxide layer. The cracks in the oxide layer propagate in the (0002)Zr plane in the zirconium matrix. The oxide layer consists of string-like zirconium oxide and zirconium hydride. The string-like zirconium oxide contains orthorhombic ZrO in addition to monoclinic ZrO
in addition to monoclinic ZrO . As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO
. As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO to monoclinic ZrO
to monoclinic ZrO in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
Asakura, Toshihide; Hotoku, Shinobu; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Masakazu; Morita, Yasuji
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(3), p.271 - 274, 2005/12
Tc extraction and separation experiments were performed basing on PUREX technique with using spent UO fuel with burn-up of 44 GWd/t. The experimental results were examined with performing calculations by a simulation code ESSCAR (Extraction System Simulation Code for Advanced Reprocessing). It was demonstrated that Tc can be almost quantitatively extracted from a dissolver solution and that Tc can also be almost quantitatively recovered by scrubbing. Further, it was clearly presented from the calculation results of ESSCAR that the extraction mechanism of Tc is dominated by the synergistic effect of Zr and U.
fuel with burn-up of 44 GWd/t. The experimental results were examined with performing calculations by a simulation code ESSCAR (Extraction System Simulation Code for Advanced Reprocessing). It was demonstrated that Tc can be almost quantitatively extracted from a dissolver solution and that Tc can also be almost quantitatively recovered by scrubbing. Further, it was clearly presented from the calculation results of ESSCAR that the extraction mechanism of Tc is dominated by the synergistic effect of Zr and U.
Nakajima, Kunihisa; Iwai, Takashi; Kikuchi, Hironobu; Serizawa, Hiroyuki; Arai, Yasuo
JAERI-Research 2005-027, 42 Pages, 2005/09
Nitride fuel pins containing inert matrix such as ZrN and TiN were fabricated for the irradiation test at JMTR, aiming at understanding irradiation behavior of nitride fuel for transmutation of minor actinides. Minor actinides are surrogated by plutonium in the present fuel pin. This report describes the preparation and characterization of fuel pellets, and fabrication of fuel pins. The irradiation for 11 cycles from May 2002 to November 2004 at JMTR was completed without any failure of fuel pins.
Amaya, Masaki; Fuketa, Toyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(11), p.1091 - 1099, 2004/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Effect of absorbed hydrogen on the stress corrosion cracking (SCC) susceptibility of unirradiated Zircaloy cladding was examined. The data obtained from literatures show that the ratios of SCC threshold stress (
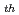 ) to 0.2% yield stress (
) to 0.2% yield stress (
 ) in unirradiated Zircaloy claddings increase with increasing hydrogen contents below 60 ppm, irrespective of the kind of Zircaloy-2 and -4. Thermodynamic calculations were carried out for the reaction between iodine gas and zirconium containing hydrogen. The results suggested that the reactions hardly occurred at increased hydrogen content and zirconium reacted with iodine gas only below 90 ppm of hydrogen. Since these tendencies correspond to those of the ratios of
) in unirradiated Zircaloy claddings increase with increasing hydrogen contents below 60 ppm, irrespective of the kind of Zircaloy-2 and -4. Thermodynamic calculations were carried out for the reaction between iodine gas and zirconium containing hydrogen. The results suggested that the reactions hardly occurred at increased hydrogen content and zirconium reacted with iodine gas only below 90 ppm of hydrogen. Since these tendencies correspond to those of the ratios of 
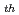 to
to 
 on the hydrogen content, it is considered that hydrogen affects the reactions between iodine gas and zirconium and reduces the SCC susceptibility of Zircaloy claddings.
on the hydrogen content, it is considered that hydrogen affects the reactions between iodine gas and zirconium and reduces the SCC susceptibility of Zircaloy claddings.